Abstract
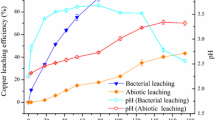
The waste stream of electrical and electronic equipment is three times faster than other municipal waste streams. Recycling of electronic waste is necessary for both reducing environmental pollution and saving natural ores. Bioleaching is known as an efficient technology for metal leaching. In most of the previous studies on the bioleaching of electronic waste, the pH of the process was adjusted daily under the optimal pH of the bacterium growth. Using acid causes increasing process costs and unsustainability of the process. In this work, the effect of daily pH adjustment on the bioleaching efficiency of electronic waste using adapted Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans was studied. Simultaneously, Cu and Ni leaching efficiency, bacterial growth characteristics, and chemical characteristics (including field emission scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, and X-ray diffraction) were discussed. The results showed that at a pulp density of 1.5% (w/v) with pH adjustment, the maximum leaching efficiency of Cu and Ni was, respectively, about 90% and 88%, while for the sample without pH adjustment, the maximum leaching efficiency of Cu and Ni was, respectively, 100% and 92%. All the results confirmed pH adjustment of the bioleaching solution is not necessary and even reduces the process efficiency.
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo F (2002) Present and future of bioleaching in developing countries. J Biotechnol 5:196–199
Akbari S, Ahmadi A (2019) Recovery of copper from a mixture of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and sulphidic tailings using bioleaching and solvent extraction processes. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 142:107584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2019.107584
Alias A-F, Ishak MB, Zulkifli SNAM, Jalil RA (2014) E-waste management: an emerging global crisis and the Malaysian scenario. Int J Environ Sci Technol 4:444–457
Arshadi M (2019) Bioleaching of E-waste. Sharif University of Technology, Tehran
Arshadi M, Mousavi SM (2014) Simultaneous recovery of Ni and Cu from computer-printed circuit boards using bioleaching: statistical evaluation and optimization. Bioresour Technol 174:233–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.140
Arshadi M, Mousavi SM (2015) Multi-objective optimization of heavy metals bioleaching from discarded mobile phone PCBs: simultaneous Cu and Ni recovery using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Sep Purif Technol 147:210–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.04.020
Arshadi M, Yaghmaei S, Mousavi SM (2018) Content evaluation of different waste PCBs to enhance basic metals recycling. Resour Conserv Recycl 139:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.08.013
Arshadi M, Yaghmaei S, Mousavi SM (2019) Study of plastics elimination in bioleaching of electronic waste using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(11):7113–7126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2120-1
Ashiq A, Cooray A, Srivatsa SC, Vithanage M (2020) Electrochemical enhanced metal extraction from E-waste, chapter 6. In: Prasad MNV, Vithanage M, Borthakur A (eds) Handbook of electronic waste management. Butterworth-Heinemann, pp 119–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-817030-4.00004-8
Baniasadi M, Vakilchap F, Bahaloo-Horeh N, Mousavi SM, Farnaud S (2019) Advances in bioleaching as a sustainable method for metal recovery from e-waste: a review. J Ind Eng Chem 76:75–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.03.047
Bas AD, Deveci H, Yazici EY (2013) Bioleaching of copper from low grade scrap TV circuit boards using mesophilic bacteria. Hydrometallurgy 138:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.06.015
Basov V (2017) These 10 mines have the world’s most valuable ore. http://www.mining.com
Brandl H, Bosshard R, Wegmann M (2001) Computer-munching microbes: metal leaching from electronic scrap by bacteria and fungi. Hydrometallurgy 59:319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-386X(00)00188-2
Colbert BW (2012) The performance and modification of recycled electronic waste plastics for the improvement of asphalt pavement materials. Michigan Technological University, Houghton
de Andrade LM, Rosario CGA, de Carvalho MA, Espinosa DCR, Tenório JAS (2019) Copper recovery from printed circuit boards from smartphones through bioleaching. TMS 2019 148th annual meeting and exhibition supplemental proceedings. Springer International Publishing, pp 837–844
Drobíková K, Rozumová L, Otoupalíková H, Seidlerová J (2015) Bioleaching of hazardous waste. Chem Pap 69:1193–1201. https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0121
FatmehsariHaghshenas H (2017) Bioleahcing of metal from electronic waste using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Sharif University of Technology, Tehran
Feng S, Yang H, Xin Y, Zhang L, Kang W, Wang W (2012) Isolation of an extremely acidophilic and highly efficient strain Acidithiobacillus sp. for chalcopyrite bioleaching. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:1625–1635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1174-1
Fundamentals of ORP measurement (2008) Application Data sheet
Ginsburg MA, Karamanev D (2007) Experimental study of the immobilization of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans on carbon based supports. Biochem Eng J 36:294–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2007.03.003
Ilankoon IMSK, Ghorbani Y, Chong MN, Herath G, Moyo T, Petersen J (2018) E-waste in the international context—a review of trade flows, regulations, hazards, waste management strategies and technologies for value recovery. Waste Manag 82:258–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.10.018
Ilyas S, Anwar MA, Niazi SB, Afzal Ghauri M (2007) Bioleaching of metals from electronic scrap by moderately thermophilic acidophilic bacteria. Hydrometallurgy 88:180–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2007.04.007
Ilyas S, Lee J-c, Kim B-S (2014) Bioremoval of heavy metals from recycling industry electronic waste by a consortium of moderate thermophiles: process development and optimization. J Clean Prod 70:194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.02.019
Islam A et al (2020) Advances in sustainable approaches to recover metals from e-waste—a review. J Clean Prod 244:118815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118815
Li L, Lv Z, Yuan X (2013) Effect of l-glycine on bioleaching of collophanite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 85:156–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.07.002
Luisser FS, Rosen MA (2009) Improving the sustainability of office partition manufacturing: balancing options for reducing emissions of volatile organic compounds. Sustainability 1:234–253. https://doi.org/10.3390/su1020234
Mäkinen J, Bachér J, Kaartinen T, Wahlström M, Salminen J (2015) The effect of flotation and parameters for bioleaching of printed circuit boards. Miner Eng 75:26–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2015.01.009
Meenambigai P, Vijayaraghavan R, Gowri RS, Prabhavathi R (2016) Biodegradation of heavy metals—a review. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 5:375–383
Mičková V, Ružičková S, Remeteiová D, Laubertová M, Dorková M (2018) Sampling and digestion of waste mobile phones printed circuit boards for Cu, Pb, Ni, and Zn determination. Chem Pap 72:1231–1238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-017-0353-y
Muravyov M (2019) Bioprocessing of mine waste: effects of process conditions. Chem Pap. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-00844-4
Nie H, Yang C, Zhu N, Wu P, Zhang T, Zhang Y, Xing Y (2015) Isolation of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain Z1 and its mechanism of bioleaching copper from waste printed circuit boards. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 90:714–721. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4363
Priya A, Hait S (2018) Feasibility of bioleaching of selected metals from electronic waste by Acidiphilium acidophilum. Waste Biomass Valor 9:871–877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-9833-0
Qiu R et al (2020) Recovering full metallic resources from waste printed circuit boards: a refined review. J Clean Prod 244:118690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118690
Rawlings DE (2002) Heavy metal mining using microbes. Annu Rev Microbiol 56:65–91
Reena G, Sangita, Verinder K (2011) FT-IR studies of e-plastic obtained from obsolete computers. J Chem Pharm Res 3:660–667
Ruan J, Qin B, Huang J (2018) Controlling measures of micro-plastic and nano pollutants: a short review of disposing waste toners. Environ Int 118:92–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.05.038
Srivastava RR, Lee J-C (2016) Leaching of gold from the spent/end-of-life mobile phone-PCBs using “Greener Reagents”, pp 7–56. https://doi.org/10.1142/9781783269907_0002
Verma A, Hait S (2019) Chelating extraction of metals from e-waste using diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid. Process Saf Environ 121:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.10.005
Wang S et al (2018) Enhanced bioleaching efficiency of copper from printed circuit boards without iron loss. Hydrometallurgy 180:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2018.07.010
Willner J (2013) Influence of physical and chemical factors on biological leaching process of copper from printed circuit boards. Metalurgija 52:189–192
Xiang Y, Wu P, Zhu N, Zhang T, Liu W, Wu J, Li P (2010) Bioleaching of copper from waste printed circuit boards by bacterial consortium enriched from acid mine drainage. J Hazard Mater 184:812–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.113
Yang X, Zhang X, Fan Y, Li H (2008) The leaching of pentlandite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans with a biological–chemical process. Biochem Eng J 42:166–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2008.06.014
Yuan Z, Ruan J, Li Y, Qiu R (2018) A new model for simulating microbial cyanide production and optimizing the medium parameters for recovering precious metals from waste printed circuit boards. J Hazard Mater 353:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.04.007
Zeng X, Wang F, Sun X, Li J (2015) Recycling indium from scraped glass of liquid crystal display: process optimizing and mechanism exploring. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:1306–1312
Zhappar NK et al (2019) Bacterial and chemical leaching of copper-containing ores with the possibility of subsequent recovery of trace silver. Chem Pap 73:1357–1367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-00688-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This project has been conducted by the deputy of research and technology of Sharif University of Technology (Award Number QA:970713) and National Elites Foundation (Award Number: 7000/9036) in Iran. The authors are thankful to Pars Charkhesh Asia company for supplying the PCBs.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arshadi, M., Yaghmaei, S. Advances in bioleaching of copper and nickel from electronic waste using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans: evaluating daily pH adjustment. Chem. Pap. 74, 2211–2227 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01055-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01055-y